How to operate a drone? Mastering this skill opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate drone racing. This guide provides a comprehensive introduction to the fundamentals of drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and safety regulations. Whether you’re a complete novice or looking to refine your existing skills, this resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We’ll explore the essential components of a drone, detailing their functions and potential points of failure. You’ll learn how to perform critical pre-flight checks, ensuring safe and successful flights. We’ll then guide you through the basic flight controls, teaching you how to take off, hover, and land your drone smoothly. Finally, we’ll delve into more advanced techniques, safety regulations, and maintenance procedures, allowing you to become a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of your drone is crucial for safe and efficient operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight capabilities, and familiarity with their functions and potential failure points is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Drone Component Overview
| Component | Function | Potential Failure Points | Maintenance Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust and control the drone’s movement. | Cracks, bends, imbalances, wear and tear. | Regular inspection for damage; replace worn or damaged propellers. |
| Motors | Convert electrical energy into mechanical energy to spin the propellers. | Overheating, burnout, motor shaft damage. | Ensure proper cooling; avoid overloading motors; inspect for physical damage. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone, processing sensor data and controlling motor speeds to maintain stability and execute commands. | Software glitches, hardware failures, sensor malfunctions (IMU, barometer). | Regular firmware updates; avoid physical shocks; calibrate sensors regularly. |
| Battery | Provides power to the drone’s components. | Over-discharge, cell imbalance, physical damage, age-related degradation. | Proper charging procedures; store in a cool, dry place; monitor voltage levels; replace aging batteries. |
| GPS | Provides location data for navigation and features like Return-to-Home (RTH). | Signal loss (due to obstructions or interference), GPS module malfunction. | Ensure clear sky visibility; check for GPS module errors; calibrate GPS regularly. |
| Camera | Captures images and videos. | Lens damage, sensor malfunction, image processing issues. | Handle with care; protect from physical damage; clean lens regularly. |
Drone Battery Types and Performance
Different drone batteries offer varying flight times and performance characteristics. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are the most common type, known for their high energy density. However, they require careful handling due to their flammability. Factors such as capacity (mAh), voltage (V), and C-rating influence flight time and power output. Higher mAh ratings generally mean longer flight times, while higher C-ratings indicate greater power delivery capabilities.
Drone Propeller Types and Performance
Drone propellers come in various sizes and designs, each affecting flight characteristics. Larger propellers generally provide more thrust and lift, but may also increase power consumption. The pitch of the propeller also plays a significant role. A higher pitch propeller will generate more thrust but consume more power. The material of the propeller (e.g., plastic, carbon fiber) also affects durability and weight.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures

A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures optimal performance.
Pre-Flight Checklist

- Check battery level and ensure it’s fully charged.
- Inspect propellers for any damage (cracks, bends).
- Power on the drone and wait for the GPS signal to lock.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Perform a visual inspection of the surrounding environment for obstacles and hazards (power lines, trees, buildings, people).
- Check local airspace regulations and ensure the flight area is permitted.
Compass and IMU Calibration, How to operate a drone
Calibrating the compass and IMU ensures accurate orientation and stability during flight. The process typically involves following the instructions provided by the drone manufacturer, often involving rotating the drone in a specific pattern. This procedure helps the drone accurately determine its position and orientation in three-dimensional space.
Pre-Flight Environmental Safety Check
A comprehensive safety check of the surrounding environment is crucial to avoid collisions and other incidents. This involves identifying potential obstacles such as trees, buildings, power lines, and people. It’s also important to be aware of weather conditions, wind speed, and visibility. Understanding local airspace regulations is also a key part of the pre-flight safety check.
Basic Drone Operation and Controls
Understanding the basic flight controls is essential for safe and controlled drone operation. These controls allow you to maneuver the drone in three-dimensional space.
Basic Flight Controls
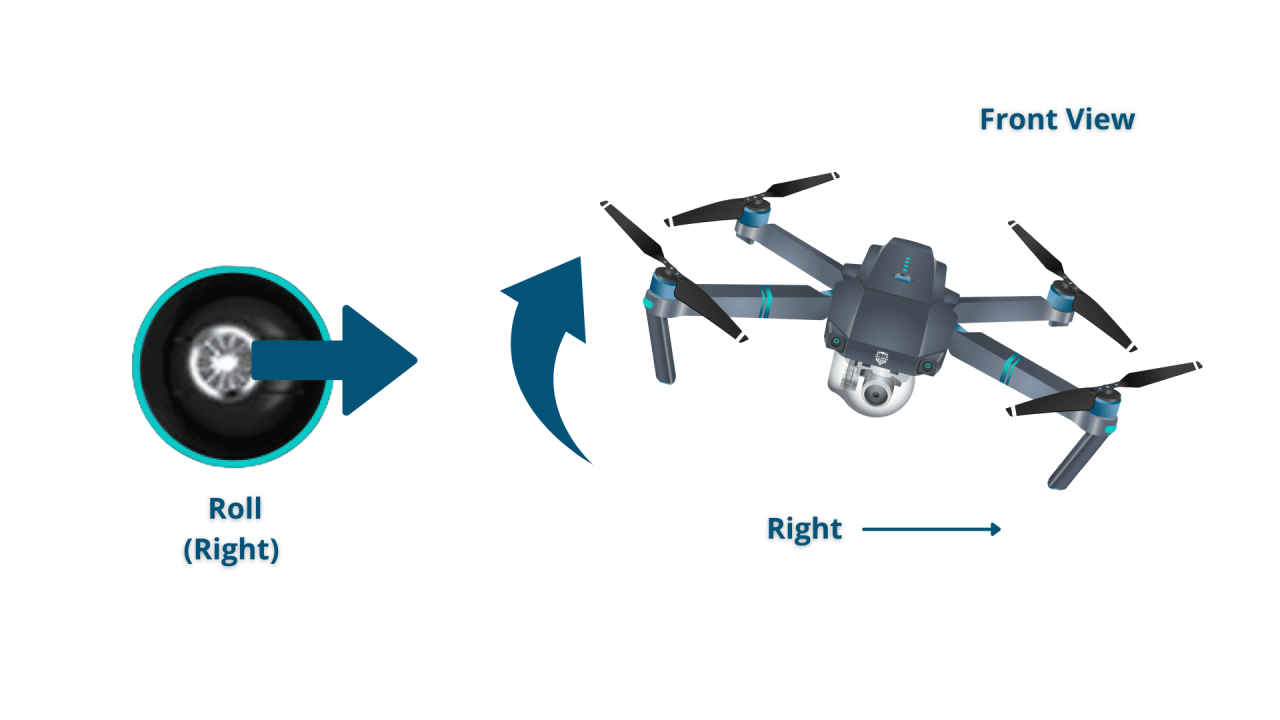
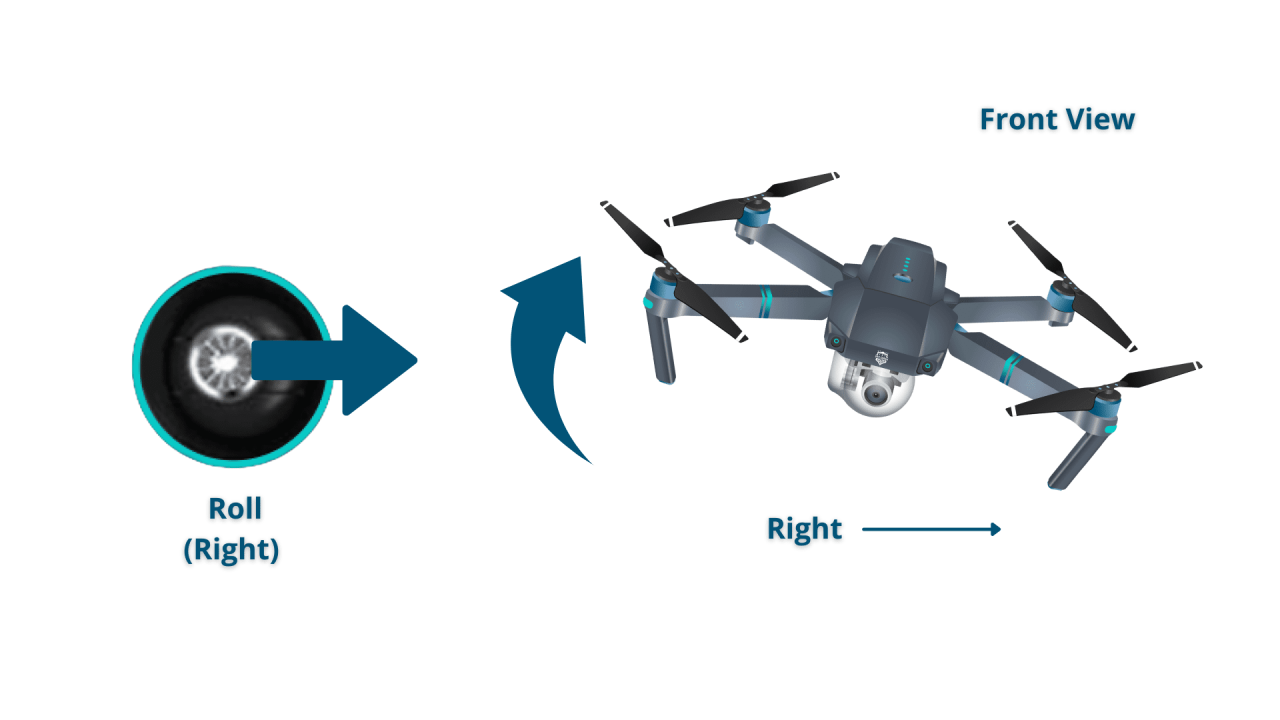
Imagine the drone as a cube. The four primary controls are:
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude. Increasing the throttle makes the drone ascend, decreasing it makes it descend.
- Yaw: Rotates the drone left or right around its vertical axis.
- Pitch: Tilts the drone forward or backward along its longitudinal axis.
- Roll: Tilts the drone left or right along its lateral axis.
By coordinating these controls, you can achieve smooth and controlled movements.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing
- Takeoff: Gently increase the throttle to lift the drone vertically. Maintain a steady throttle to achieve a stable hover.
- Hovering: Maintain a constant throttle to keep the drone at a fixed altitude and position. Make small adjustments to the pitch, roll, and yaw controls to maintain stability.
- Landing: Gradually decrease the throttle to bring the drone smoothly back to the ground. Avoid sudden movements during landing.
Beginner Flight Plan
A simple flight plan for beginners could involve taking off, hovering for a few seconds, moving a short distance forward and backward, then returning to the takeoff point before landing. This allows practice with basic controls and altitude adjustments. Gradually increase the complexity of the maneuvers as your skills improve. Remember to always maintain a safe distance from obstacles and keep the drone within visual line of sight.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers and Features: How To Operate A Drone
Once comfortable with basic operation, you can explore advanced flight modes and camera features to enhance your drone experience.
Advanced Flight Modes
Many drones offer advanced flight modes such as:
- Waypoint Navigation: Allows you to pre-program a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Enables the drone to automatically return to its takeoff point if the signal is lost or the battery is low.
- Follow-Me Mode: Allows the drone to automatically follow a designated subject, such as a person or vehicle.
These modes greatly enhance the drone’s capabilities and simplify complex flight operations.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. Successfully piloting requires practice and a grasp of fundamental techniques, and a great resource for beginners is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills allows for safe and effective drone operation, opening up a world of possibilities for aerial photography and videography.
Drone Camera Systems
Drone cameras vary significantly in features and quality. Key features include resolution (measured in megapixels), field of view (FOV), image stabilization, and video recording capabilities (resolution, frame rate). Some drones also offer features such as obstacle avoidance and intelligent tracking.
Drone Sizes and Types
Drones come in various sizes and configurations. Quadcopters are the most common type, featuring four rotors. Hexacopters, with six rotors, offer greater stability and redundancy. Larger drones generally have greater payload capacity and flight time, but are less maneuverable than smaller drones. The choice of drone depends on the specific application and user needs.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount. Adherence to safety precautions and regulations is crucial to avoid accidents and legal issues.
Drone Safety Precautions
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Avoid flying near airports, heliports, or other restricted airspace.
- Be aware of weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds or inclement weather.
- Never fly your drone over crowds or populated areas.
- Respect the privacy of others and avoid filming without permission.
- Always check battery levels before and during flight.
- Keep your drone away from power lines, tall buildings, and other potential hazards.
Drone Regulations
| Regulation Category | Specific Requirement (Example) | Penalty for Non-Compliance (Example) | Where to Find More Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airspace Restrictions | No flight within 5km of an airport without permission. | Fine, license suspension. | Your local aviation authority website. |
| Registration | Drone registration may be required depending on weight and use. | Fine, confiscation of drone. | Your national civil aviation authority. |
| Privacy | Obtain consent before filming individuals or private property. | Legal action, fines. | Data protection and privacy laws in your region. |
Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation involves respecting the privacy of others, adhering to all applicable laws and regulations, and avoiding hazardous environments. Always prioritize safety and responsible flying practices.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition and extending its lifespan.
Basic Drone Maintenance
- Clean the drone body and propellers after each flight to remove dirt and debris.
- Inspect the propellers, motors, and other components for any damage.
- Check the battery terminals and connections for corrosion.
- Replace worn or damaged parts as needed.
- Store the drone in a cool, dry place to protect it from extreme temperatures and humidity.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Some common drone problems and their solutions include:
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully or replace with a fully charged one.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure clear sky visibility, move to an open area, or calibrate the GPS.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect motors for damage, check motor connections, or replace faulty motors.
- Drone not responding: Check battery level, ensure controller is paired, and check for software glitches. Consider a firmware update.
Regular Drone Maintenance Checklist
A regular maintenance schedule should include:
- Daily: Clean the drone and inspect for damage.
- Weekly: Check battery voltage and calibrate the compass and IMU.
- Monthly: Perform a more thorough inspection of all components and replace worn parts as needed.
Operating a drone responsibly requires a combination of technical skill and a strong understanding of safety regulations. By mastering the fundamentals of drone operation, performing thorough pre-flight checks, and adhering to all relevant regulations, you can unlock the full potential of this versatile technology while ensuring the safety of yourself and others. This guide has provided a foundation for your drone piloting journey; remember to continue learning and practicing to enhance your skills and expand your aerial adventures.
General Inquiries
What is the best drone for beginners?
Several user-friendly drones are excellent for beginners. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization, return-to-home functionality, and intuitive controls. Research reviews and compare features before making a purchase.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
It’s best to charge your drone battery after each flight. Avoid completely depleting the battery to extend its lifespan. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging times and procedures.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering controls. Learning the fundamentals is crucial for safe and effective flights, and a great resource to help you learn is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This guide will help you confidently navigate the complexities of drone piloting and ensure you’re ready to take to the skies responsibly.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal during flight?
If you lose GPS signal, immediately switch to manual control and attempt to bring the drone back to a safe landing area. Many drones have a “return-to-home” function that can assist in this situation.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by region. Check with your local aviation authority to determine if registration is required and what the process entails. Failing to register your drone when required can lead to legal penalties.